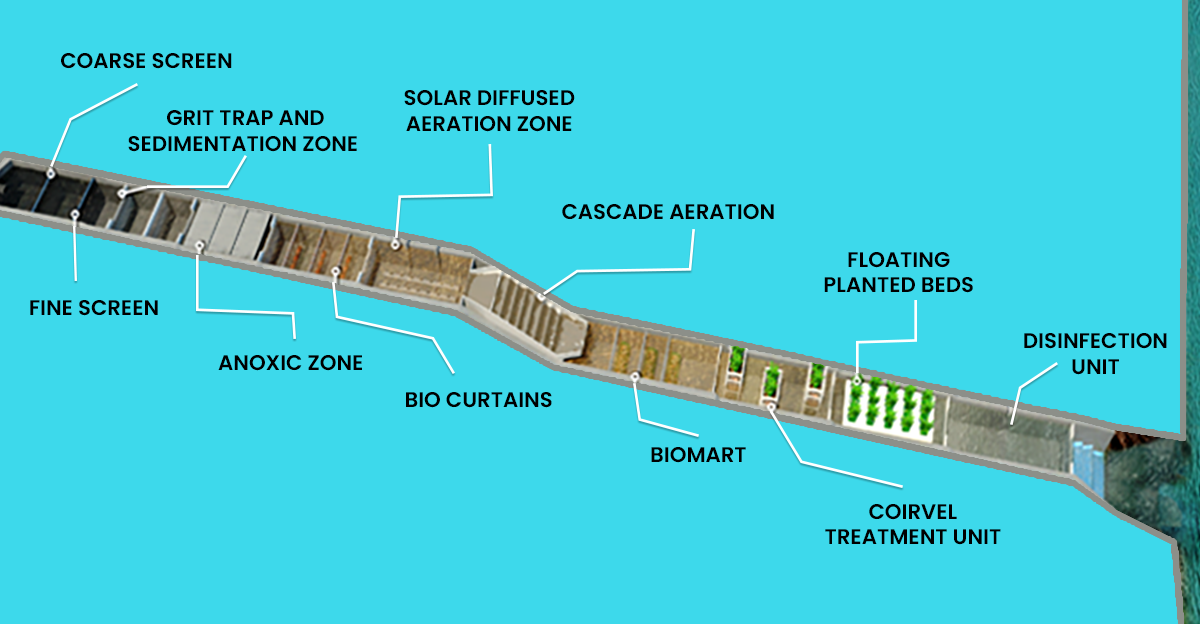
In-situ drain treatment entails the following steps:
Phytoremediation
Phytoremediation is a bioremediation method that employs diverse plant species to remove, transfer, stabilize, and/or eliminate pollutants in soil and groundwater. Phytoremediation is the removal of organic chemicals and nutrients from wastewater via bio-sorption/uptake by pollution-tolerant aquatic plants (such as algae, water hyacinth, duckweeds, and others) growing in the wastewater. Such plants commonly develop in the littoral zones on each side of the drain.
Constructed Wetlands (CWs)
CWS also employs Phytoremediation methods. It combines microbial bioremediation, phytoremediation, and root-zone treatment, as well as the advantages of an oxidation pond and physical filters. Constructed wetlands (CWs) are scientifically established and widely used as an alternative and supplementary solution to traditional sewage treatment systems across the world. A well-designed engineered wetland system will operate on the same principles as STP but with more microbial variety associated with varied plant species that successfully biodegrade organics and other contaminants in sewage while using no energy.
Microbial Bioremediation
In microbial bioremediation, a suitable number of enzymes and microorganisms, as well as fungi, plants, and/or periodic or continuous dosing of specific waste is added to the wastewater mass. The majority of the material treated by microorganisms is organic; a limited number of inorganic materials and metals are also taken up as nutrients. Enzymes are directly used in biochemical therapy. It should be noted that anaerobic microorganisms require more time to break down the waste than aerobic microbes do.